The img tag
Basic syntax for the img tag
The img tag is the simplest and most common way to display an image in an html page.  It requires a
It requires a src attribute, which indicates where the browser will find the image, and an alt attribute, which provides a textual version of the image for screen-readers.
img src="path/to/image.jpg" alt="My image"
An img element is, by default, an inline element, so it will wrap with other inline elements on the page.
Sizing an img
img tags can be sized with CSS. Like other elements, you can add an id, class, or other attributes as you see fit in order to assist with styling. Generally, it is best to set only width or height, not both. If you set only one, the browser will set the other automatically in order to maintain the aspect-ratio of your image source file.
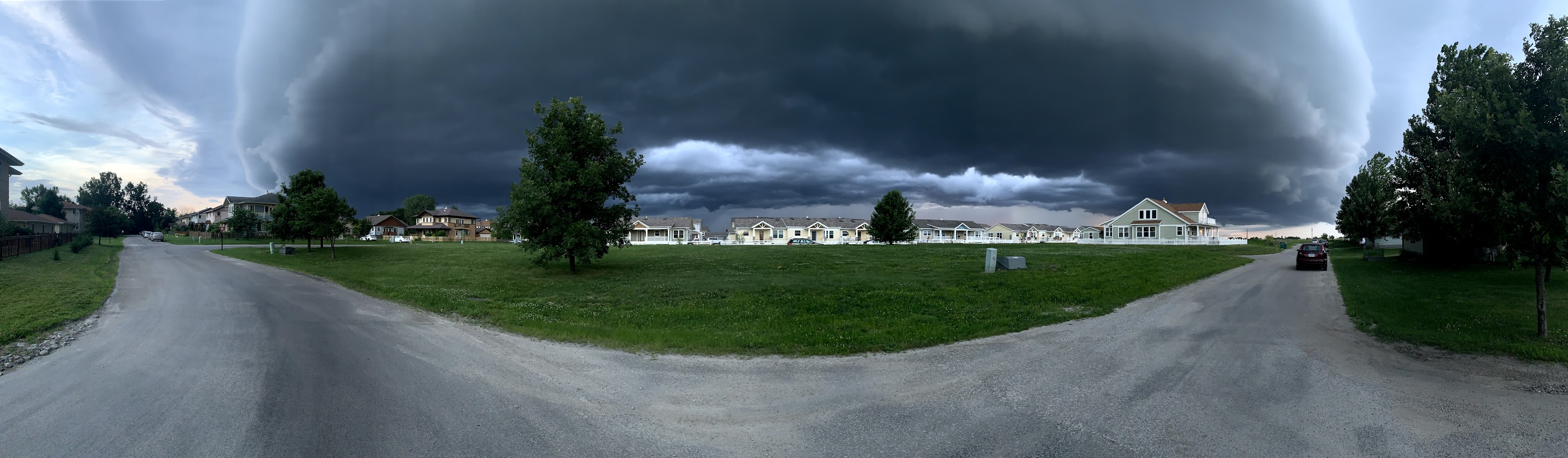

Cropping an img
Sometimes your source image doesn't match the aspect-ratio of the space you need to fill. What if we want to put our wide image into a square? First, let's try just setting both width and height.

The image is stretched! Not what we wanted. We need to tell the image to be cropped, not stretched.
Now the image is cropped, instead of stretched. The cover value tells the browser to scale the image proportionally such that it just covers the entire area of the img tag, but no larger. (You can also use the contain value, which scales the image proportionally to fit entirely inside the area of the imgtag.) The image will be centered by default, but the center is not really the best part of this particular image, so let's reposition it.
The object-position value can have two parts, the first for the horizontal position, the second for vertical position. We can use words like left, right, and top, or numerical values like 100px or 20%.
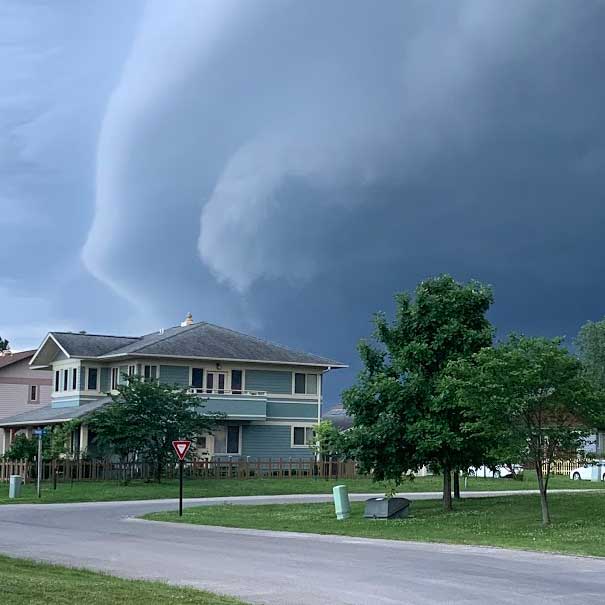


 36KB
36KB
 138KB
138KB
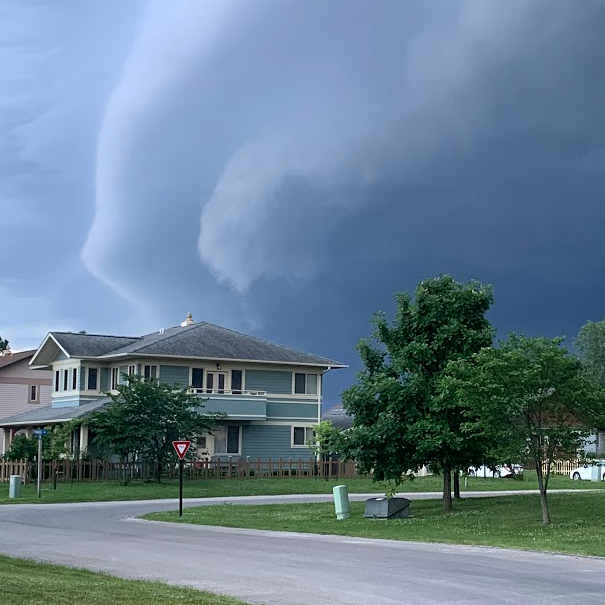 422KB
422KB
